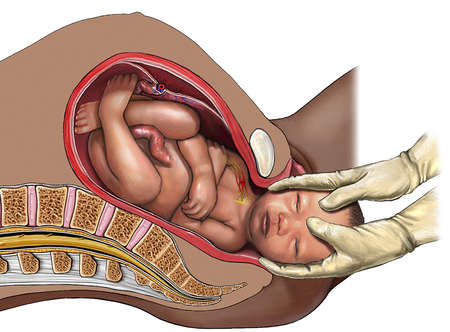
Brachial plexus Injuries
Obstetric Brachial plexus injury or Bp injury (synonyms are: shoulder distocia, or brachial plexus palsy) in newborn is a complication associated with overextension, rapture or roots avulsion from spinal cord of brachial plexus nerves. Frequently the injury is associated with medical malpractice (watch video of a lawyer explaining the cause of Bp injuries). The statistics shows that Bp injuries happen in 0.1-4 % of all life deliveries (frequency depends on country), but could be predicted on the basis of simple estimations of expected baby weight, mother's body architecture, and predispositions (previously having a child with Bp injury; diabetes in mother). Recently development of the algorithm to calculate risks associated with obstetric Bp injury was reported.
A number of Bp injuries in newborns are healed by themselves in 2-4 months after birth; those which can not be cured spontaneously are usually associated with nerve raptures and avulsion from spinal cord. The good solution in young children is micro-neurosurgery with grafting or nerve rerouting with often complete restoration of a limb function. Such a recovery in children is more successful than in adults, however it takes longer. Excellent neuroplasticity of immature child’s central nervous system (CNS) allows functional regeneration in contrast to adults.
Also in children, Bp injuries happen during sports activity (e.g baseball) and in motor car accidents. Due to small weight of a child comparing to an adult, children experience more severe Bp injuries in motor car accidents as compared to obstetric Bp injuries (more cases of nerve avulsion). However, still functions restoration is often more successful than in adults.
Bp injuries in adults are often devastating and in 5% of cases happen as a result of motorcycle accidents. Even though neurosurgery is technically advanced today, full recovery may require several surgeries. Also adults in 80% of cases develop severe complications - excruciating pain similar to phantom-limb pain which luckily mayresolve after function restoration; however the surgery has to be scheduled as soon as possible after an injury for successful function restoration. The afferentiation pain is so pronounced that a number of patients have to undergo dorsal risoectomy to be able to focus on their limb function restoration. In it interesting to note that children literally never develop such a pain (only several cases reported).
The Source for the Background Image: http://blog.nj.com/southjersey_impact/2007/09/large_fatal.jpg
Bilotkach Kateryna, UCI, BME 240, Spring-2009